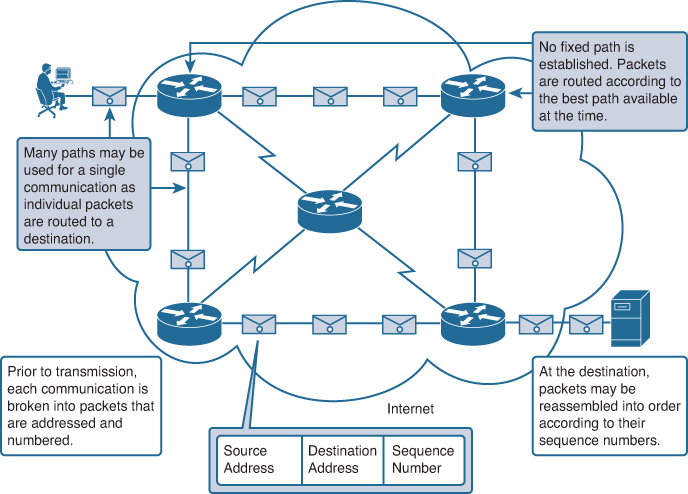
In a digital-first world, each and every piece of digital information transmitted over the internet is delivered in small bundles of data, called packets. This includes emails, messages you've sent via apps, websites you've accessed, video calls and much more.
These data packets contain the information itself as well as metadata identifying traffic source, content, destination, and other valuable details. To ensure that data is routed to the proper destination, a process called packet filtering monitors and manages the data, as well as network traffic patterns in real time.
See what's holding you back from your desired collaboration destination with Collab Compass.

Conventional packet filtering, however, is simply not enough to ensure network security. This means organizations need a tool that can perform Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) on their entire network, as part of their network analytics processes.
DPI explained
Deep packet inspection (DPI), is a form of packet filtering used every day by organizations and your internet service provider (ISP) to detect and prevent cyber-attacks, monitor traffic patterns, combat malware, optimize servers, and analyze user behavior.
Conventional packet filtering only examines the packet's header, so the value of DPI is that it locates, identifies, classifies and reroutes or blocks packets with specific data or code payloads.
So while stateful packet inspection only evaluates packet header information, such as source IP address, destination IP address, and port number, deep packet inspection looks at a more comprehensive range of data and metadata associated with individual packets.

As packets reach an inspection point, DPI intercepts any non-compliance to protocol, viruses, spam, and other anomalies, and blocks the packet from passing through the inspection point.
In today's digitally driven business world, with the imminent threat of hackers and other cyber-attacks, many organizations rely on deep packet inspections as part of their network security, and as a firewall to ensure the safety of their network and users.
How does deep packet inspection work?
As mentioned, conventional packet filtering doesn't have the capabilities of a DPI which can scan the contents of a message and identify the specific application or service that sent it. You can also reroute network traffic from a specific Internet Protocol (IP) address range or online service (like Facebook or Twitter) by programming filters.
Traditional firewalls didn't always have the processing power necessary to perform more in-depth inspections on large volumes of traffic in real time. These days, however, technological advancements mean that DPI can perform more advanced inspections to check both packet headers and data.
Tech leaders and network administrators have welcomed deep packet inspection technology as an important tool to help cope with the increase in the rising volume, complexity and frequency of internet-related threats. DPI is mainly used by firewalls with intrusion detection systems.
Deep packet inspection uses
Deep packet inspection functions are vital for network security, because it they determine whether a particular packet is moving through network traffic towards the right destination.
Unlike conventional network packet filtering, in which packets are sorted based on the source and destination, deep packet inspection goes beyond examining the incoming packets to pick up protocol anomaly, analyze, locate, and block the packets if and when required.
A DPI system also offers packet-level analysis to identify the root-cause of application or network performance issues. It’s considered one of the most accurate techniques to monitor and analyze application behavior, network usage issues, data breaches and more. Additionally, deep packet analysis also helps with:
-
Measuring business-critical applications with high network latency
-
Improving application availability and meet SLAs
-
Generating reports on historic data and performing forensics
Deep packet inspection can also help copyright holders such as record labels by blocking their content from being downloaded illegally. DPI can also be used to serve targeted advertising to users, lawful interception, and policy enforcement.
The benefits of deep packet inspection
Deep packet inspections offer several important benefits when it comes to a corporate network or any organization's network performance.
DPI is an important network security tool
By analyzing packets other than just the packet header, DPIs are able to catch threats or block detected attacks that may be hidden in the contents of the data. This allows an organization to more readily identify usage patterns, and block malware, data leaks, and other security threats to the network and its end users.
DPI provides additional options for managing network traffic flows
Deep packet inspection allows for the programming of rules that look for specific types of data and identify high and low priority packets. In this way, deep packet inspection can give preference to higher-priority or mission critical packets throughout the data stream, and pass them through the network first, ahead of ordinary browsing packets or lower priority messages.
These rules and policies, once clearly defined by an organization, allow the network to detect if there are prohibited uses of approved applications.
Deep packet inspection can also be used to inspect outbound traffic as it attempts to exit the network. This means that organizations can create filters designed to prevent data leaks. You can also use deep packet inspection to learn where your data packet is going.
Predetermined rules guide how DPI handles packets in real time
All packet information, from the header to its contents, are checked and automatically handled based on the pre-programmed rules that your team puts in place. This way your system can automatically sort, filter, and prioritize each packet without slowing down the network.
Deep packet inspection provides the ability to do something about traffic that fits a profile, such as generating an alert for dropped or lost packets, or limiting the bandwidth available to that traffic.
Read our comprehensive guide to network packet loss here
Deep packet inspection techniques
Here are some of the primary techniques used in deep packet inspection in network management:
Pattern or signature matching
A firewall with Intrusion Detection System (IDS) capability analyzes each packet against a database of known network attacks. The IDS looks for specific patterns that are known to be malicious and blocks the traffic if it finds such a pattern. The disadvantage of the signature matching approach is that it can only be effective if signatures are updated regularly.
Additionally, this method only works against known threats or attacks. As new threats are discovered daily, ongoing signature updates are critical to ensure that the firewall can detect the threats and continue to keep the network safe and secure.
Heuristic and Behavior Analysis
Understanding an application or protocol begins with studying its behavior. For example, measuring packet sizes and the timing between packets etc. Even if the protocol or application changes its signature, the behavior is likely to remain the same. For example, Voice over IP (VoIP) traffic usually starts with session initiation and then many smaller-sized UDP packets are used to deliver the call traffic.
Protocol anomaly
The protocol anomaly technique is also used by firewalls with an IDS but here, it follows a default deny approach, where the firewall determines which content/traffic should be allowed based on protocol definitions. So the difference is that unlike signature matching, this method also protects the network against unknown attacks.
Intrusion prevention system (IPS)
IPS solutions can block detected attacks in real time by preventing malicious packets from being delivered based on the contents of the packets. So, if a particular packet represents a known security threat, the IPS will proactively deny network traffic based on a defined rule set. However, the database needs to be updated regularly with information about new threats.
The downside of IPS is the risk of false positives, although these can be curtailed by establishing proper baseline behaviors for network components, creating conservative policies and custom thresholds, and regularly reviewing alerts and logged incidents to improve network monitoring and alerting.
Limitations and challenges of deep packet inspection
All technology has its challenges and limitations that sit alongside its benefits. In the case of deep packet inspection, there are three main issues:
-
While DPI functionality provides protection against existing vulnerabilities, it can also create new vulnerabilities in the network. While deep packet inspection is effective against buffer overflow attacks, denial-of-service attacks and malware threats, it can also facilitate attacks in those same categories.
-
Deep packet filtering can increase the complexity of existing firewalls and other security software. And, to remain optimally effective, DPI requires periodic updates and revisions, which can cause extra admin headaches for security teams.
-
DPI is notorious for reducing or interfering with network speed and performance because it creates network bottlenecks and increases the burden on firewall processors for data decryption and inline inspection
Stay in control with network performance management tools
As hybrid working is now an integral of life, new technology and a landslide of data passes through networks every minute, and the demand for a seamless user experience increases. The need for high up-time, fast problem resolution, and intelligent insight has never been more critical. Part of the strategy to achieve this is to have all-seeing eyes on your network at all times.
The IR Collaborate suite of hybrid-cloud performance management tools can protect your network by bringing together reliability, agility, and innovation to solve the complexities of managing your critical technologies.
By providing end-to-end visibility across your entire multi-vendor UC network, IR Collaborate can quickly identify, troubleshoot and resolve any issues with our monitoring and performance management tools.
Our solutions provide complete visibility, proactive network management and troubleshooting, analytics and insights tailored to your organization, an all of this in real time, across your on-premises, cloud or hybrid environments.