In a working world, where a bricks-and-mortar office is no longer the norm, organizations need the right tools to manage their employees and to monitor their networks’ efficiency and security from anywhere, without being physically present.
Enterprise mobility has created infinite possibilities for business growth and diversification through the use of mobile technologies. The primary goal of enterprise mobility solutions is to enhance productivity, efficiency, and security for both employees and the organization in an increasingly mobile-centric business world.
Almost 33 million Americans, or about 22 percent of the workforce, will work from home by 2025, and this means business owners will need an effective RMM strategy to remotely monitor and secure employee endpoint devices and applications, as well as ensuring seamless system performance.
RMM is an essential element of a modern IT infrastructure, and preventative maintenance now overrides the previous break-fix approaches that kept IT technicians from more productive, higher value tasks.
In this guide, we'll explain how organizations can deploy remote monitoring management strategies that provide complete visibility into an organization's IT ecosystem from a central location.
Through remote management, you can proactively detect and resolve issues using real time data, manage devices and user configurations from a single console, and navigate network complexities to ensure smooth business operations.
What is Remote Monitoring & Management?
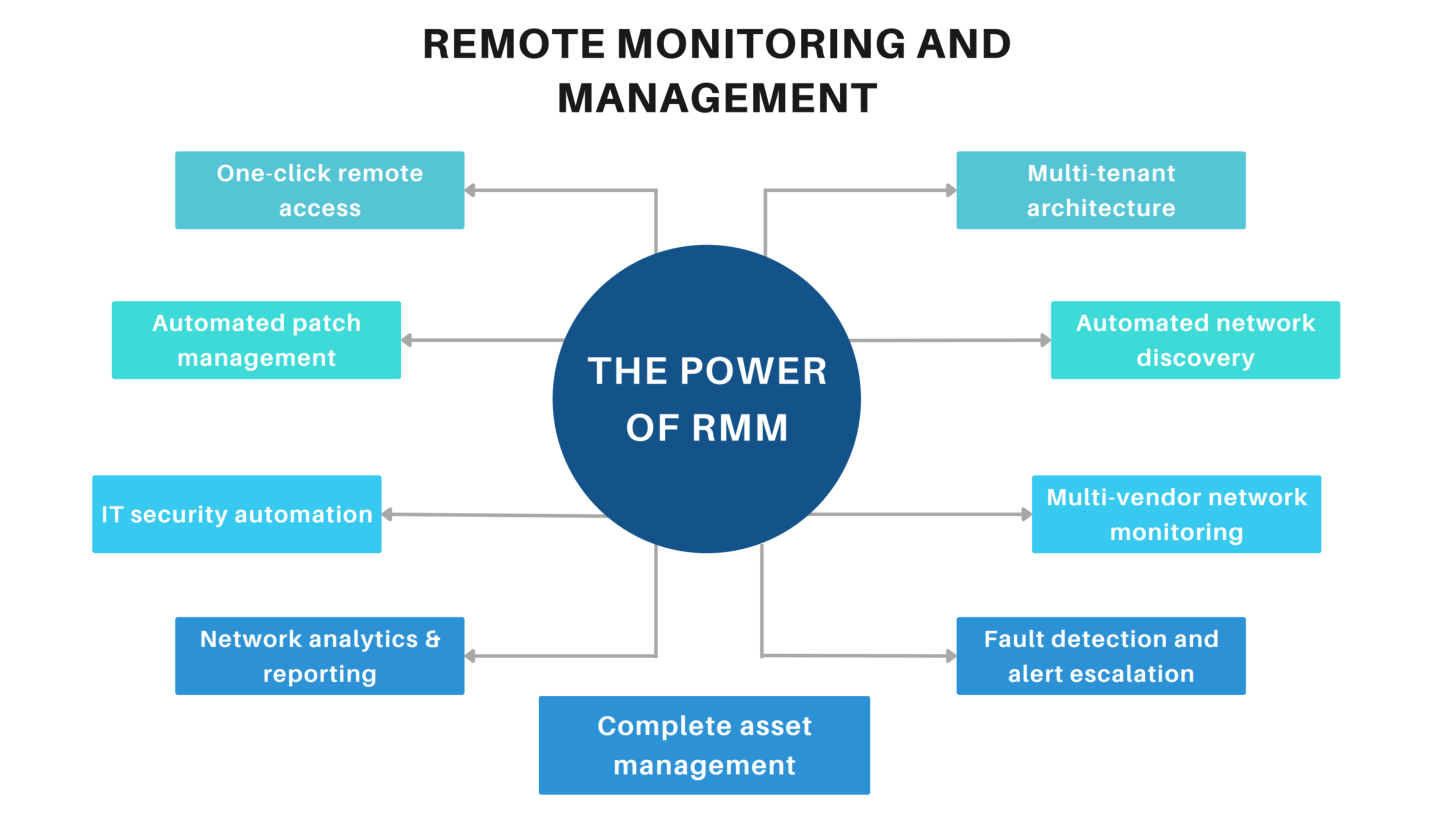
Remote Monitoring Management (RMM) is a term that encompasses the use of IT software which allows a Managed Service Provider (MSP) to monitor a workforce’s mobile devices, client endpoints, and networks by remote control.
For enterprise organizations, RMM software is essential to deploy and actively manage third-party endpoint security products and backup solutions to ensure employee and customer data security.
What are the capabilities of RMM software?
-
RMM technology enables proactive monitoring of the health of networks and systems. Remote access enables IT admins to identify issues before they become critical and result in costly downtime. An RMM tool allows for preemptive solutions that can not only significantly minimize downtime but maintain the user experience, and ensure client satisfaction.
-
RMM software enables automation and scalability. When organizations can manage and automate routine tasks, such as updates and patch management, it can ensure that systems don't become vulnerable to known issues or cyber threats. This saves time and allows for better allocation of network resources.
-
RMM provides a centralized management dashboard from which various networks and systems can be monitored and managed, enabling better secure endpoints. This centralization makes it easier to identify and rectify issues fast, which is vital in maintaining the operational efficiency.
-
RMM provides better security management to help safeguard networks and systems against potential security threats. This is critical for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the reputation of websites in the eyes of search engines.
-
RMM software can send customized alerts for different events, enabling quick responses to potential issues. This proactive real time approach can prevent minor issues from escalating into significant problems, negatively impacting SEO performance.
A Brief history of RMM
Before the advent of RMM, IT management was largely reactive (break-and-fix) and usually administered on-site, by in-house technicians.
It was the rise of managed service providers (MSPs) in the late 1990s and early 2000s that accelerated the development of RMM into the sophisticated(and complex) platforms we see today.
The pre-RMM era
Technicians would need to physically visit the hardware to install, update, or repair systems, a time-consuming, costly and inefficient process that often ended in frustration and limited resolution to problems. The need for a more proactive and efficient IT asset management became apparent.

Image source: Freepik
The introduction of Network Management Tools
The first step towards what would become RMM was the development of network management tools in the late 1980s and early 1990s, allowing IT professionals to monitor network performance and troubleshoot issues from a central location. Mostly in the early days, they were primarily focused on large networks and not capable of managing endpoints or providing the comprehensive management capabilities that a modern RMM solution can offer.
The rise of MSPs
The complexity of IT environments and the need for businesses to focus on their core operations spurred the concept of managed services in the late 1990s. MSPs offered a subscription-based model where businesses could outsource their IT management needs with tools that could provide remote monitoring and management capabilities at scale. This led to the development of the sophisticated RMM platforms available today.
More about the benefits of an RMM Solution
A robust RMM strategy will boost IT reliability and efficiency for every organization, providing some of the key benefits we've already touched on including proactive monitoring, reduced downtime and improved client satisfaction.
Let's look at the advantages of RMM more closely.
Real-time monitoring and alerts management
Before the rise of remote working and RMM, when an employee had a technical issue, they would need to wait for an IT team member to identify and fix the problem. This would amount to the loss of potentially hours of productivity, especially if the issue was affecting multiple employees at once.
It goes without saying that the best way to solve a technical issue is to prevent it from happening in the first place. RMM software monitors all the devices on your network, as well as the applications your team uses for any potential problems.
If any warnings or issues come up, the software will alert the MSP, who can monitor the issue more closely or remotely control the situation in real time, before it becomes a major issue.

IT automation and scripting
The maintenance of an organization's devices or software can be time-consuming, so before RMM, they would often mute or delay an update notification until the next day. Continuous postponement often led to missing important updates and patches.
RMM frees up IT experts to work on more important issues and allows employees to maintain their devices without interrupting their work time.
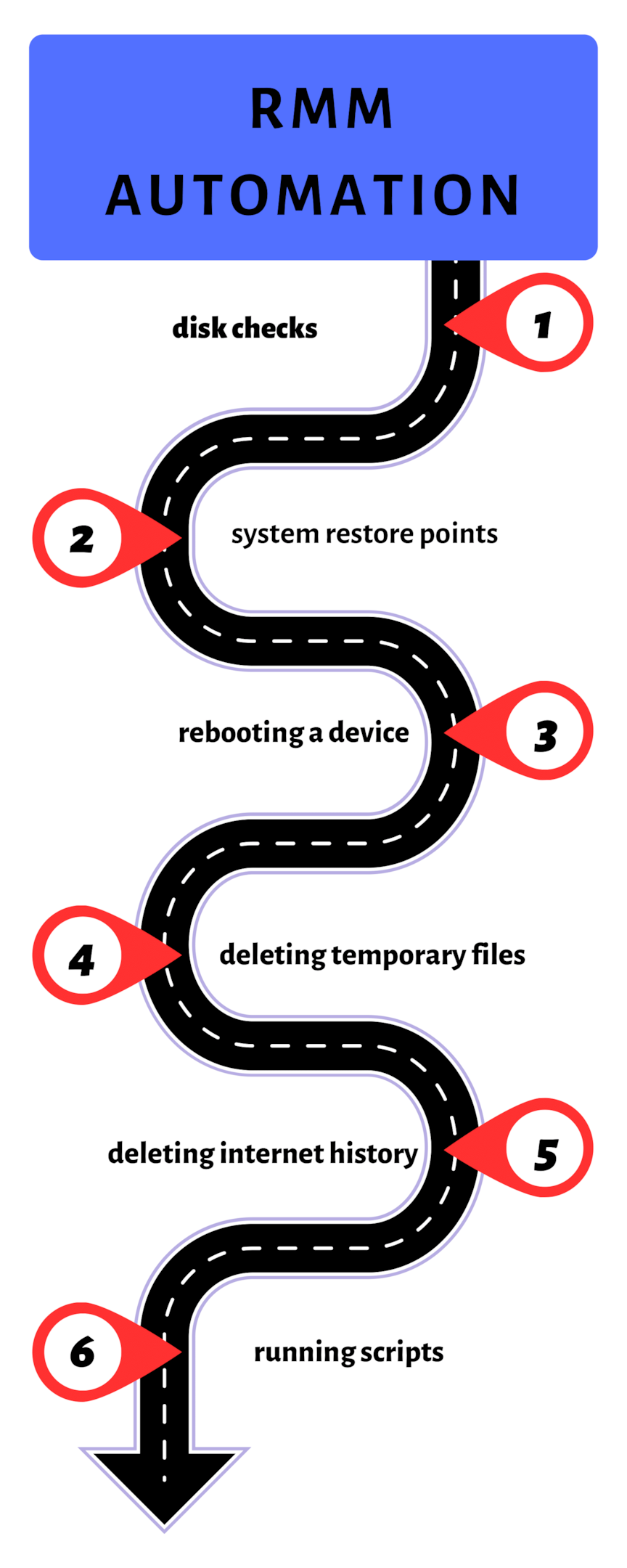
Types of automated tasks
-
Running disk checks
-
Creating system restore points
-
Rebooting a device
-
Deleting temporary files
-
Deleting internet history
-
Running scripts
Reporting and analytics
A RMM can not only automate and monitor tasks, but can also collect all the data from systems and processes, and turn it into an analytical report.
IT teams and managers can then use these reports to get a clear view of projects, allowing more informed decisions for the organization. These reports can be generated automatically through a scheduling system or on demand.
Type of reports
-
System and device health
-
User experience
-
System audits
-
Licensing
-
Software inventory and upgrade history
-
Patch feedback
Expanding client base and offering better service
As well as all the benefits covered above, RMM tools are a major factor in facilitating scalability, as they allow MSPs to expand their client base without affecting their operational costs and overheads.
By utilizing RMM tools, MSPs can also offer a broader range of remote management services, enhancing their value proposition and attracting more clients.
Customer satisfaction and loyalty
Remote monitoring and management plays a vital role in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty by ensuring that business systems remain stable and perform at optimal levels. When systems run smoothly with minimal downtime, it enables businesses to provide better customer services, which in turn fosters positive experiences and builds trust and loyalty over time.
Importance of RMM Customer Support
Customer support is a crucial factor to consider when deciding on the right RMM software. Having access to responsive, knowledgeable support can make a significant difference in quickly resolving issues and minimizing disruptions.
With a high percentage of today’s workforce working from home or locations outside the office, MSPs must have the ability to maintain their networks remotely. A good RMM strategy enables MSPs mobile device management capabilities to troubleshoot and fix issues.
Through one pane of glass and a centralized dashboard, they can see any CPU, process, memory and other errors on the device which makes it easier to pinpoint the problem, and reducing overall labor and downtime.
Image source: Datto RMM
RMM buyer's guide for MSPs
With the capability of RMMs to remotely monitor thousands of devices at scale, it means that MSPs have revolutionized the IT services industry.
While RMMs come with a vast array of feature sets and core capabilities, not every RMM platform is the right fit for every MSP. Here a few things to consider.
Ease of onboarding and integration
A good RMM system should seamlessly integrate with your existing technology stack. It should be able to quickly deploy agents onto all devices in your clients' network and collect the relevant asset information you need.
Network device monitoring
While implementing an RMM platform for large enterprise organizations with hundreds of endpoints, it isn't just enough to monitor the PCs, but to also cover devices like printers, scanners, routers, and switches. The data from these devices could provide critical insights and reveal security vulnerabilities and threats.
Security management
Manually updating antivirus software on local devices is simply not a feasible aspect of remote management. MSPs need to be able to run security patches and install updates within their client networks remotely through RMM software.
Note: The security requirements for MSPs vary across different countries and regions, so it's important to ensure that remote monitoring solutions consider local compliances before purchasing.
RMM Pricing
RMM services are typically priced using a flat-rate, monthly recurring revenue model. However, there are many factors that can contribute to the average RMM pricing structure, including:
-
Number of mobile devices, laptops, workstations, servers, virtual machines, and networking devices being monitored
-
Number of users who need access to the RMM tool
-
The features and functionality you intend to use
-
Whether you need support, setup, onboarding, and/or training
-
Hosting considerations
Ease of scaling
A great RMM tool helps MSPs to scale effectively. Scaling doesn't just mean increasing the number of devices (or endpoints), but also in terms of managing any additions or changes in device functions over time. It also greatly helps to have criteria in place to ensure the monitoring quality isn't affected at scale.
RMM-PSA integration
A powerful RMM tool will deeply integrate with an existing PSA system. A unified PSA-RMM system will help streamline operations (ticketing, project management, etc.,) and dramatically improve user experience and customer satisfaction through quicker resolution times, and better team management.
PSA-RMM integration would also help MSPs create better reports and comprehensive dashboards, and facilitate multiple channels of communication between technicians and clients.
Prioritizing Security
Handling sensitive user and business data is part of the job description for IT departments. Choosing RMM platforms with robust security features is integral to safeguarding classified information.
RMM features and key capabilities should include encryption, multi-factor authentication, and the ability to enforce compliance across all devices and networks to safeguard against external threats and internal vulnerabilities.
Multi-platform support
Every client network is unique and operates differently depending on their industry. Many organizations have IT networks that also run on different operating systems. To effectively manage these networks, MSPs should make sure that their RMM software integrates with these various operating systems. This ensures that all networks are properly monitored and managed, regardless of their individual structure and function.
24/7 Remote Support
Reliable customer support is vital, especially when enterprise organizations have complex IT systems and networks.
Evaluate the quality of customer support, including availability (24/7 support), types of support offered (phone, email, live chat), and take into consideration any reviews that may reveal the software supplier's reputation for responsive service.
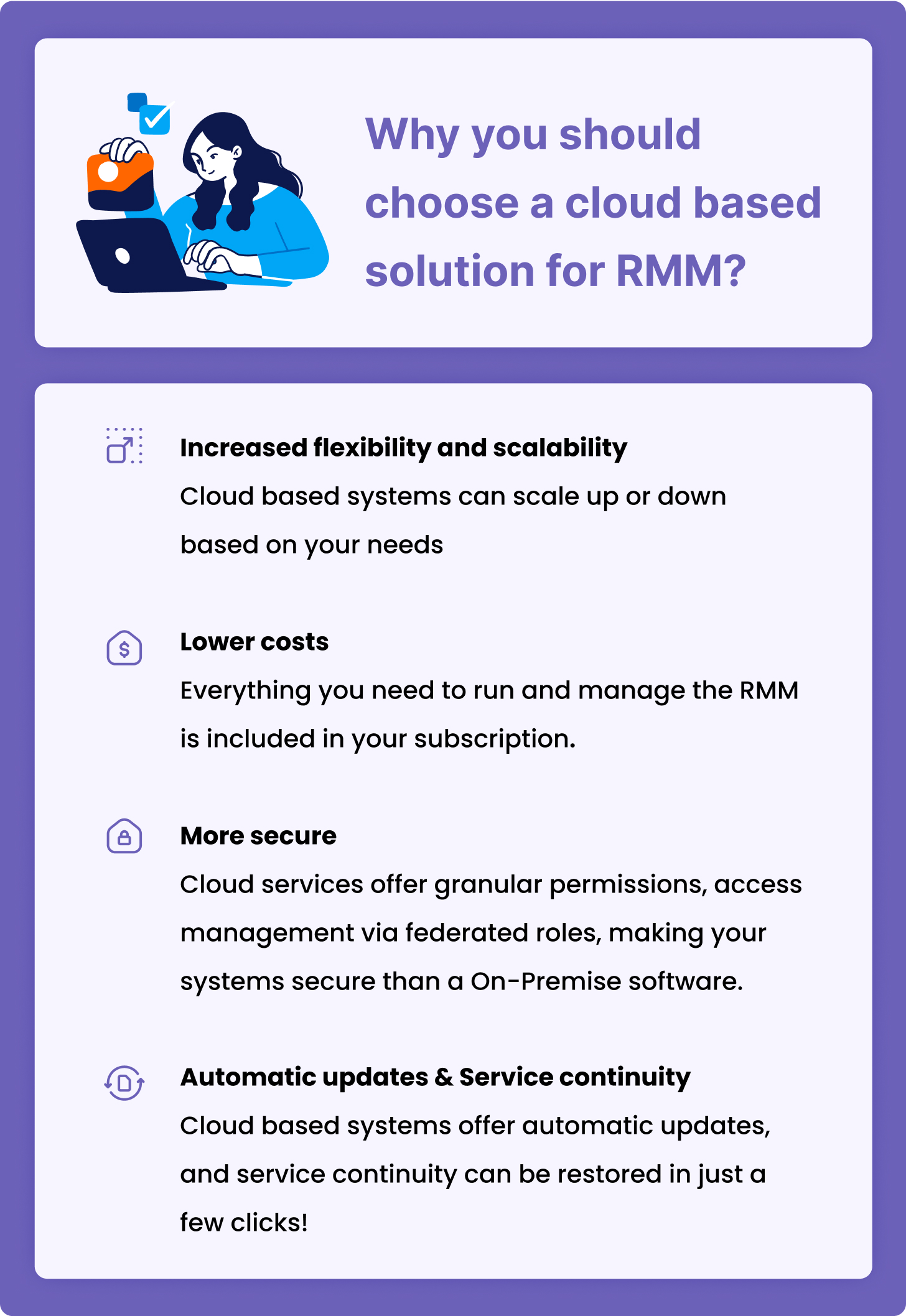
On-premise vs cloud based remote monitoring and management solutions
Choosing between on-premise and cloud-based RMM tools depends on various factors such as business needs, security requirements, budget, and IT infrastructure. Here’s a comparative analysis to help you decide which might be better for your situation:
On-premises tools
Many MSPs use on-premises versions of RMM software which has benefits including:
Control - with on-premise, you have complete autonomy over the service delivery, management of its data, and who can access it.
Ownership - you deploy and run the software
Data protection - Opting for on-premises keeps all your data in your own data center. Third-party suppliers will not have access to your data.
Access control - access to the RMM platform and its data is always guaranteed on your network; you're not dependent on the internet for the whole experience.
Image source: SuperOps
Cloud based tools
With cloud-based RMM solutions, MSPs can proactively administer and monitor an organization's IT environment from anywhere in the world. Simply put, cloud-based RMM solutions can effectively and efficiently control client-side IT operations without visiting the physical location. Cloud-based tools have helped many organizations raise their levels of IT support.
Image source: SuperOps
Find out more about How Managed Service Providers Can Drive Digital Transformation
How IR Collaborate can help
With the relentless focus on remote working, enterprise organizations are increasingly aware that infrastructure problems can slow their digital innovation, so they're turning to MSPs to manage endpoints within their IT environment.
This shift creates requires that MSPs adopt a continuous innovation mindset.
IR Collaborate's suite of world-class third party RMM solutions play a significant role in cost optimization and releasing resources for strategic value creation.
Across on-premises, hybrid cloud and multi-vendor environments, IR Collaborate for service providers can help deliver deep insights, comprehensive visibility, and customer-specific reports. This adds more value, and helps MSP confidently meet SLAs.
With real-time alerting, rapid troubleshooting, and end-to-end visibility across your entire UC ecosystem, IR Collaborate helps service providers accelerate time-to-revenue, reduce service delivery costs, confidently manage multiple customers, deliver customer satisfaction, and ensure repeat business – ultimately protecting your bottom line.