For any organization, the last thing you want to hear is that the network is down. Worse still, when your computer network crashes, it creates a slew of problems for IT teams, and the pressure is on as the clock ticks to reduce the amount of downtime.
Every minute that users can't access the network results in frustration for users and network admins, not to mention loss of productivity, customer attrition, and ultimately, a potentially disastrous loss of revenue.
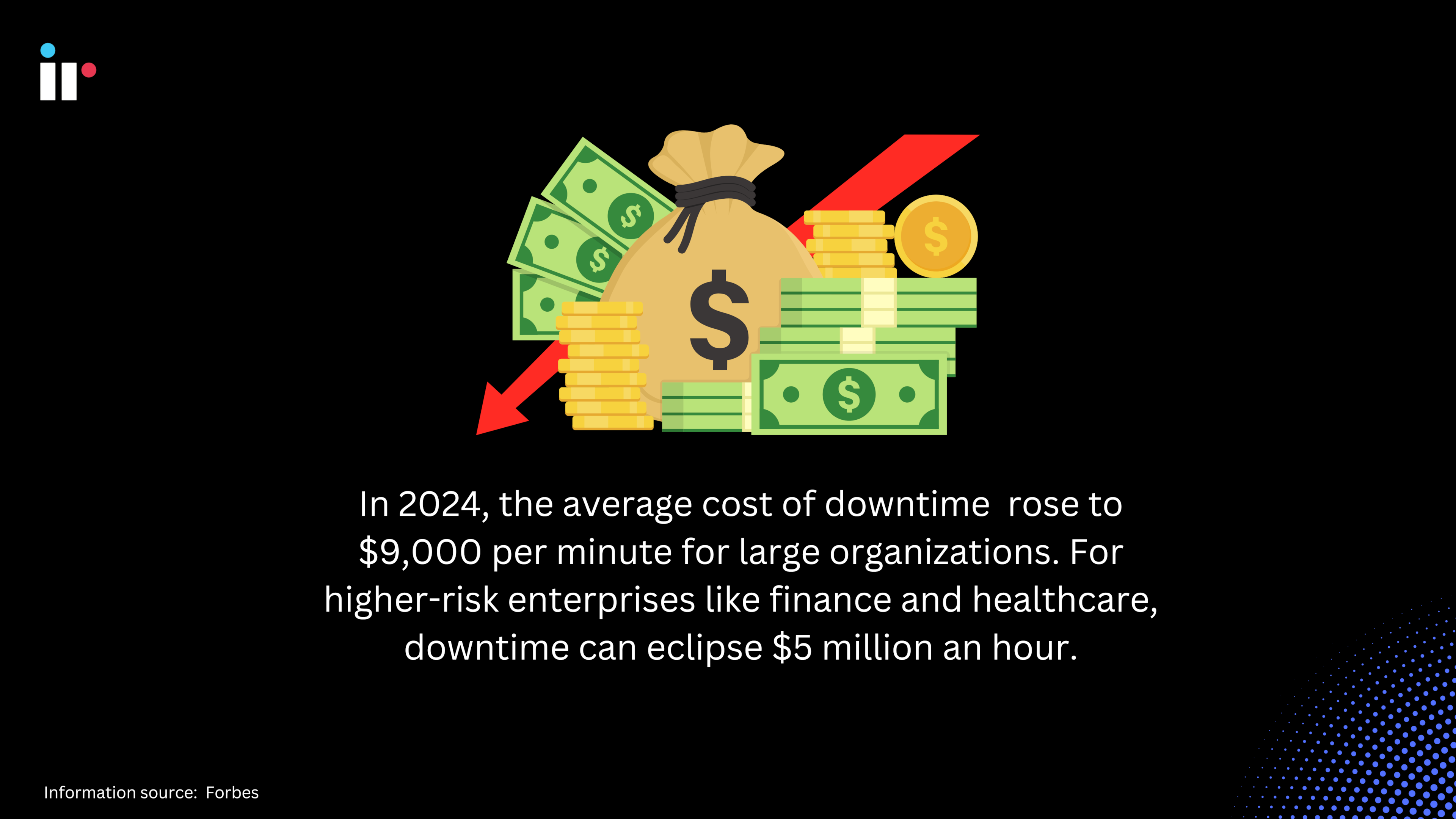
Info source: Forbes Tech Council
This unfortunate scenario can be almost completely avoided with the right network monitoring solutions in place.
In this definitive guide, we'll cover the key factors to consider when choosing network management tools to monitor and manage your entire network infrastructure.
We'll discuss the importance of proactive management tools to give network admins a holistic view of your virtual machines, network devices, servers, workstations, operating systems, cloud networks and more.
For every enterprise organization, flawless network performance is the holy grail. In an ideal world, all network devices would function as they should, network traffic would be bottleneck-free and all network components including operating systems, hardware and software would tick along trouble-free 24/7.
But the truth is, today's communication and collaboration networks are complex environments, and becoming more so every day. With remote and hybrid working models a part of every day working life, scattered locations, multiple devices and disparate wireless networks, sub-par network performance is an unfortunate part of working life for every enterprise organization.
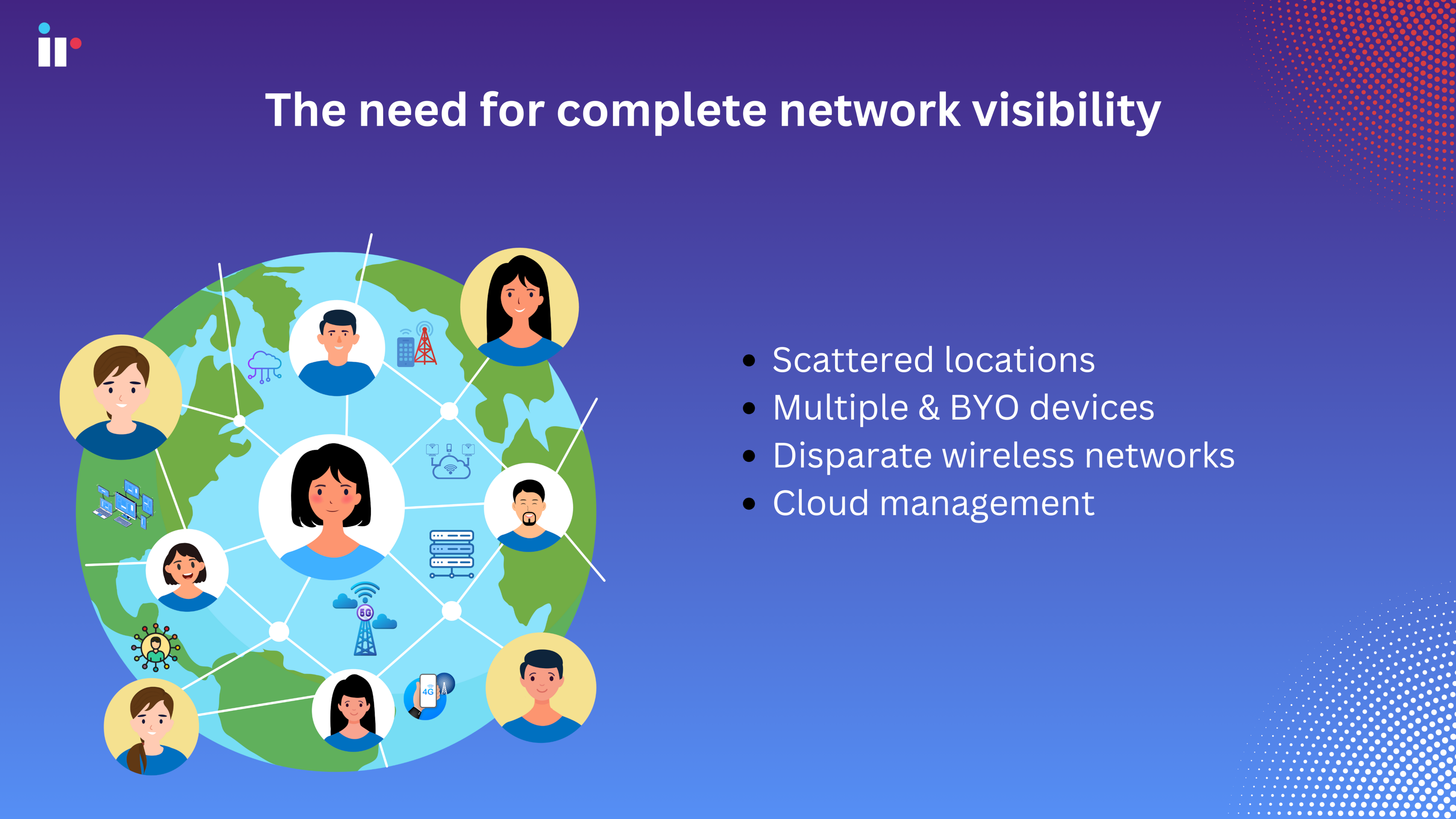
The question is...can network failures be prevented? They absolutely can, with complete visibility into your entire network infrastructure - using the right network management software.
The primary purpose of a world class network management tool is to deliver an efficient, secure and reliable network to your organization and all your end users, so let's find out about the tools, metrics and best practices for a fully optimized, healthy network infrastructure.
Why is network monitoring important?
Network monitoring is no longer considered a nice-to-have for enterprise organizations, or indeed SMBs, particularly now that remote working has become a cornerstone of working culture.
Without network monitoring tools, all of your network devices and other components are at risk of failure which can be time-consuming and difficult to fix after the fact.
Much like on the highways, network traffic can become bottle-necked for various reasons, meaning that both incoming and outgoing traffic slows or stops altogether, causing network failures and problems for network administrators.
So how do you stop this from happening, or at least reduce the negative impact? The answer is effective network monitoring with the right network performance monitoring tools.
What exactly is network monitoring?
Network management tools are crucial to the seamless functioning of every organization.
Every network infrastructure is different when it comes to specifics. But all networks have components such as VMs, routers, servers, network devices, mobile devices, switches and much more. When you include the added complexity of dispersed locations, security threats, and the addition of multiple network 'BYO devices' the repercussions of just one of these components not working creates potentially massive problems.
Network monitoring with the right network management tool can track and manage all of these components, as well as key performance indicators like CPU utilization and network bandwidth, issues that affect network performance like latency, jitter and packet loss.
A network monitoring tool enables organizations to be more proactive and to reduce downtime by allowing them to respond more quickly to issues before they seriously impact the end-user.
In short, an advanced network monitoring system gives organizations visibility across their entire network in real-time to maintain and optimize the availability of each of their network components.
For more information on finding the best monitoring software
Read our comprehensive guide
How does network monitoring work?
Network monitoring not only provides visibility into all of the network's layers and components, which helps engineers troubleshoot issues at any layer, but it uses sophisticated software tools to continuously analyze and report on a network's performance and health.
Like an all-seeing-eye, the best network monitoring tool can:
Deploy monitoring agents - that are placed on network devices, such as access points, switches, firewalls, routers, and servers.
Use protocols - like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), and NetFlow to gather metrics.
Ping system ports - to check for parameters that are outside of established thresholds.
Generate alerts - if a device reports a parameter outside of the established threshold, a network monitoring tool can automatically generate alerts.
Collect data - a network management tool collects data on bandwidth usage, packet loss, jitter and latency that can negatively impact a network's performance and user experience.
Analyze data - Once collected, a network management tool can analyze the data to identify and troubleshoot problems with the network, and predict possible future issues.
Networks enable the transfer of information between computers and applications. Computer systems rely on a series of functions to send and receive data, and in order for this to happen, the data needs to go through an Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) to break it down and interpret it. As it goes through the OSI it utilizes different network protocols, from the physical layer to the application layer.
The best network monitoring tools provide visibility into all of these layers as well as the various components that make up a network, ensuring that engineers can troubleshoot network issues at any point within the network.
What are features of the best network monitoring software?
A network monitoring system tracks the health of a network across all of its hardware and software layers through comprehensive infrastructure monitoring. It also has integrated features including network configuration management.
IT engineers use network monitoring software to proactively address and troubleshoot network outages and failures. So rather than responding in a reactive, or 'break-fix' manner (after the fact), most network monitoring tools can track network health proactively and continuously, along with every connected network device, before network issues occur.
Network monitoring systems provide complete visibility, or network mapping into an organization's networks. This enables not only early detection of network issues, but a clear picture of all network elements to determine exactly why and where problems are occurring, creating invaluable historical data that can be used to prevent future issues.
Find out more about choosing the best network management software
There are four key features that your network performance monitor should ideally provide:
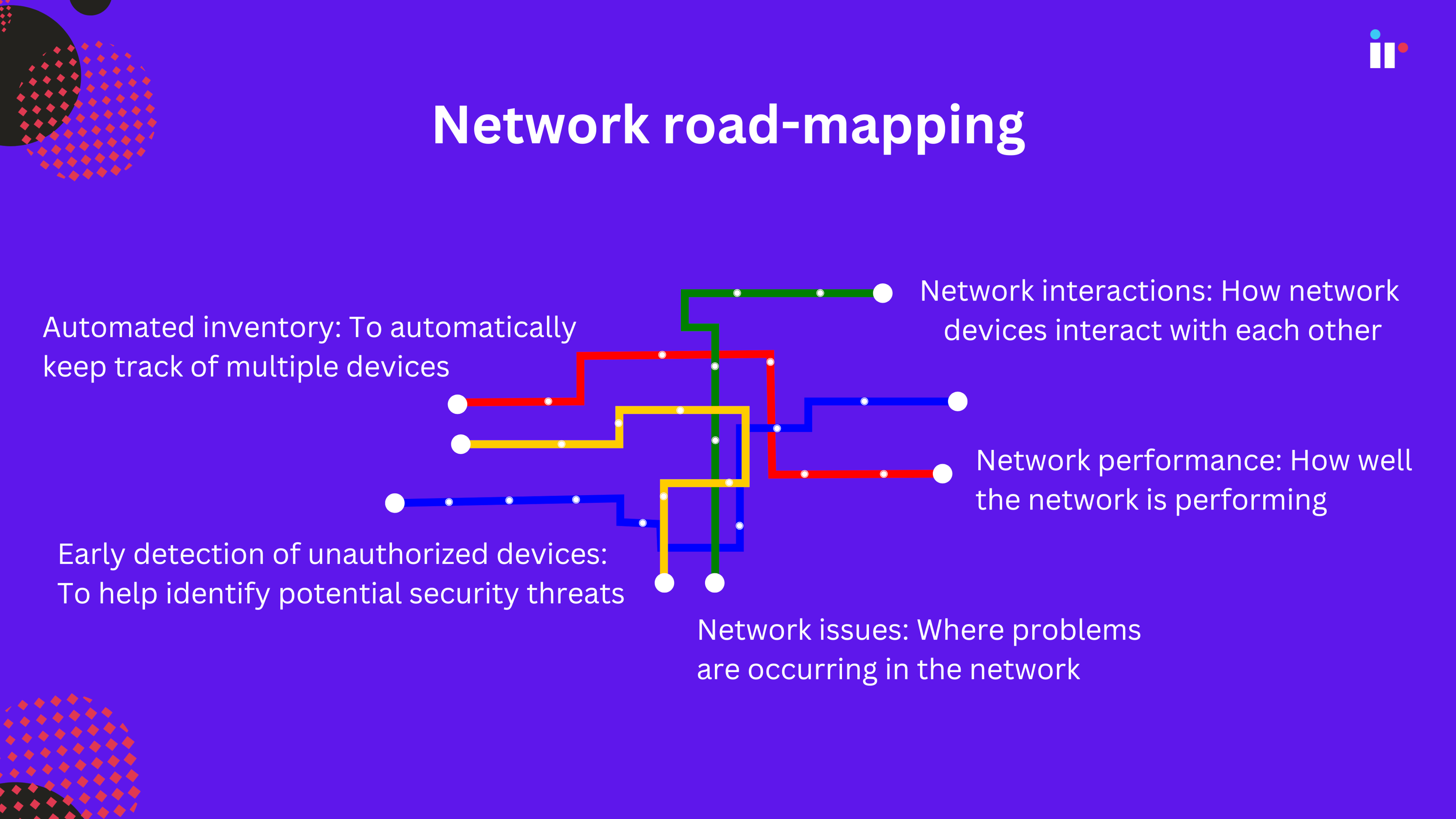
1. Network road-mapping
An efficient network management tool needs the ability to automatically identify and map all devices and connections within a network.
Network road-mapping is the process of documentation and visual representation of a network's physical connectivity, including all network devices and their interconnections.
The goal is to gain visibility into the network and IT infrastructure to better understand network configuration management, as well as what might be causing problems.
This feature saves valuable time and resources, and ensures that every component of your network is accounted for, including those that might have been overlooked or forgotten. Ideally your network performance monitor should have these features:
-
Automated inventory feature
To automatically keep track of multiple devices, saving considerable time for IT admins, and reducing the risk of human error.
-
Dynamic network mapping
To enable a visual representation of the network across the entire network, simplifying troubleshooting and offering a better understanding of the network structure.
-
Early detection of unauthorized devices
To help identify potential security threats by detecting new and possibly unauthorized devices on the network.
2. Monitoring in real time
An effective network performance monitor is like an all-seeing-eye, ensuring that your network runs smoothly and meets the evolving demands of your organization. The ability to monitor a network's performance, including network traffic in real-time is pivotal for every enterprise organization.
IT professionals can see what’s happening on their network at any given moment, allowing for immediate response to issues as they arise. Your network's performance monitor should ideally allow:
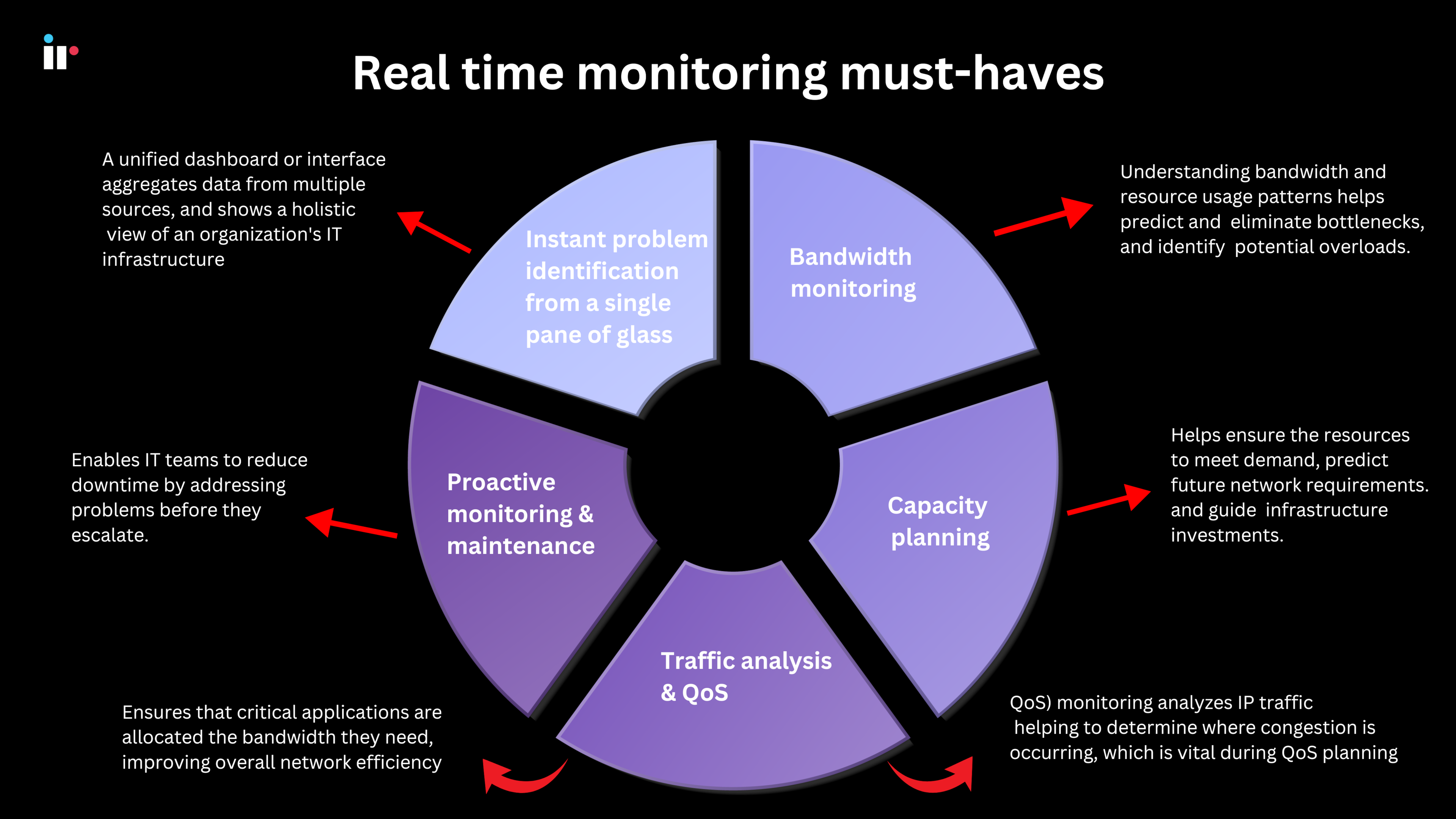
Instant problem identification from a single pane of glass
Network monitoring software must have the ability to quickly pinpoint the source of traffic bottlenecks, a network's performance issues or failing devices. But seeing your entire network through a Single Pane Of Glass (SPOG) is just as vital.
A unified dashboard or interface aggregates data from multiple sources, and shows a holistic view of an organization's IT infrastructure. This approach simplifies monitoring in increasingly complex and distributed IT environments.
Bandwidth monitoring
Network management software helps to understand bandwidth and resource usage patterns, predicting and eliminating bottlenecks, as well as identifying potential overloads. If you can understand how bandwidth and resources are being used, and identify which applications or users are using the most bandwidth it can help anticipate capacity needs and plan for bandwidth provisioning.
Monitoring bandwidth also helps identify malicious or malformed traffic, such as sudden traffic spikes.
Proactive monitoring and maintenance
Proactive monitoring in real time enables IT teams to reduce downtime by addressing problems before they escalate. But proactive maintenance is a multifaceted process, and involves 5 key components that work together to ensure a network's optimal performance and security.
- First, there's the monitoring solution itself. The software continuously tracks and scans the network, collecting data on various performance-related metrics and picking up any anomalies that could indicate a potential issue.
- Secondly is the alert system. When the monitoring tool identifies a potential issue, it sends an alert to the designated respondents, usually the IT team or service provider. This allows teams to address the issue before it impacts a network's performance or security.
- The third component is the reporting system, providing IT teams with detailed information on network status and performance. This is important to identify trends and subsequently make informed decisions about network management protocols.
- The incident response plan is the fourth component. This outlines the steps that the IT team should take when an alert is triggered, enabling a swift and effective response to potential issues.
- The final component is the continuous improvement strategy, involving regularly reviewing and updating the monitoring strategy to ensure it remains effective as network usage grows and evolves.
By preventing network issues, proactive network monitoring can also offer cost benefits by reducing the need for emergency repairs and maintenance.
Traffic analysis and QoS
Ensures that critical applications are allocated the bandwidth they need, improving overall network efficiency.
Quality of service (QoS) monitoring analyzes IP traffic throughout the network, helping to determine where congestion is occurring, which is vital during QoS planning, and as a troubleshooting tool.
Capacity planning
Real-time monitoring is important for capacity planning because it helps organizations ensure they have the resources they need to meet demand.
The best network management software helps to predict future network requirements and is helpful in guiding infrastructure investments. It also helps organizations predict current and future demand, and maximize utilization of their resources, which can lead to improved profit margins.
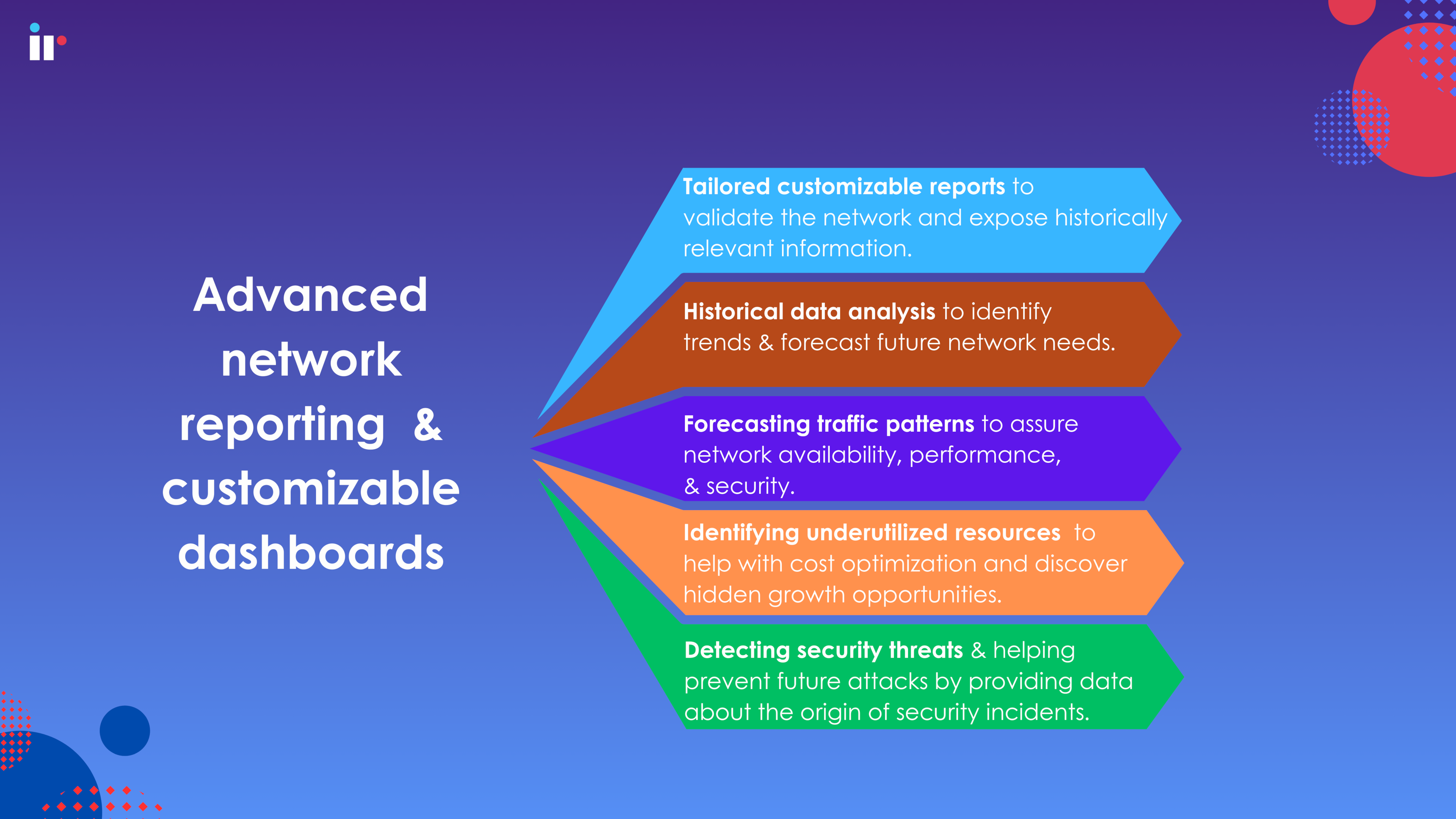
3. Advanced network reporting and customizable dashboards
An advanced network management tool collects performance data and offers comprehensive reporting capabilities and intuitive dashboards.
The best monitoring tool can monitor multiple networks across different sites and unify the data, providing a centralized view of the entire network infrastructure.This allows for the easy interpretation of complex data and helps administrators make informed decisions through:
Customizable reports
Your network performance monitor should provide tailored reports to meet your organization’s specific needs, so they need to be fully customizable to help validate the network, identify trends, and expose historically relevant information.
This information can be used to reorganize or scale the network, provide regulators with proof of compliance, make informed business growth decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and take corrective action when needed.
Historical data analysis
Enables IT administrators to identify trends, and long term data, which helps forecast future network needs. Historical data is important for monitoring a network because it provides a basis for comparison and can help identify issues and trends. It can help with:
Forecasting traffic patterns
It's crucial to understand and forecast where and how network traffic flows to assure network availability, performance, and security. This helps network engineers anticipate future demands and plan for peak loads.
Identifying underutilized resources
By identifying what is being used and when, organizations can make better use of their available capacity and achieve their goals more effectively. This can help with cost optimization.
Additionally, by understanding resource utilization levels, network admins and managers can take a fresh look at resources and potentially discover previously hidden growth and revenue increasing opportunities. They can also make more informed decisions about hiring, training, or reallocating resources.
Detecting security threats
Advanced network reporting can be instrumental in pinpointing suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks.
The top network monitoring tools can help identify threats by detecting suspicious network device connections and locations, and identifying anomalies. They can monitor software execution, and identify outliers that might be threats.
Advanced management tools can also help prevent future attacks by providing information about the origin of security incidents.
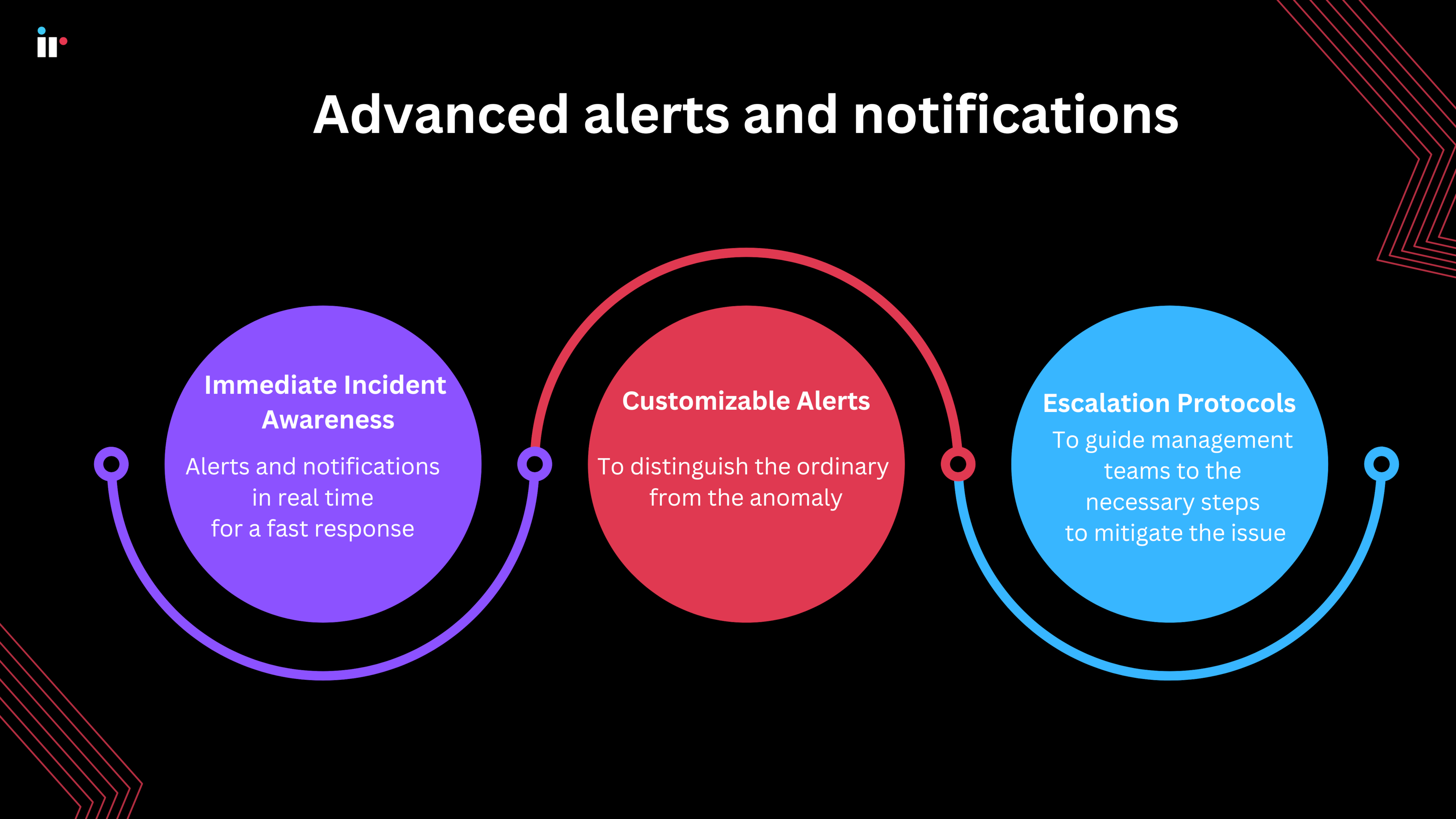
4. Advanced alerts and notifications
What we consider the 4th most important feature to look for in network management software is a robust system for alerts and notifications.
While monitoring continuously tracks and analyzes network data to provide actionable insights, alerts serve as targeted signals that indicate when attention is needed. The best management tools provide proactive alerts, not just about detecting issues but about enabling timely interventions to prevent network disruptions.
This crucial feature ensures that network administrators are immediately notified of any network problems or issues, allowing them to take action quickly to reduce downtime. Your network management software should provide:
Immediate Incident Awareness
Your network management software should allow comprehensive configuration management to provide alerts and notifications in real time for a fast response to network issues or failures.
With in-depth intelligent network alerting capabilities, network management software should provide the detailed information you need, including interface and node name, the date and time when the alert occurred, and the alert severity, so network managers know exactly where to start troubleshooting.
Customizable Alerts
In every organization's network, the effectiveness of an alerting system hinges on its ability to distinguish the ordinary from the anomaly, ensuring that every alert requires attention.
Establishing clear and actionable alert thresholds is essential, and key to a robust network management strategy. Network managers should be able to use the monitoring and management software to tailor alert conditions and thresholds to suit their network’s unique requirements.
Escalation Protocols
Monitoring and management software have protocols in place ensuring that critical alerts reach the right people quickly, to streamline and expedite the resolution process.
This involves setting alerts based on conditions that significantly impact the health or security of the network and require immediate intervention. Each alert should guide network management teams towards the necessary steps to mitigate the issue.
This approach helps to avoid the common problem of overwhelming users with FYI alerts that lead to alert fatigue and potentially dilute the urgency of truly critical issues.
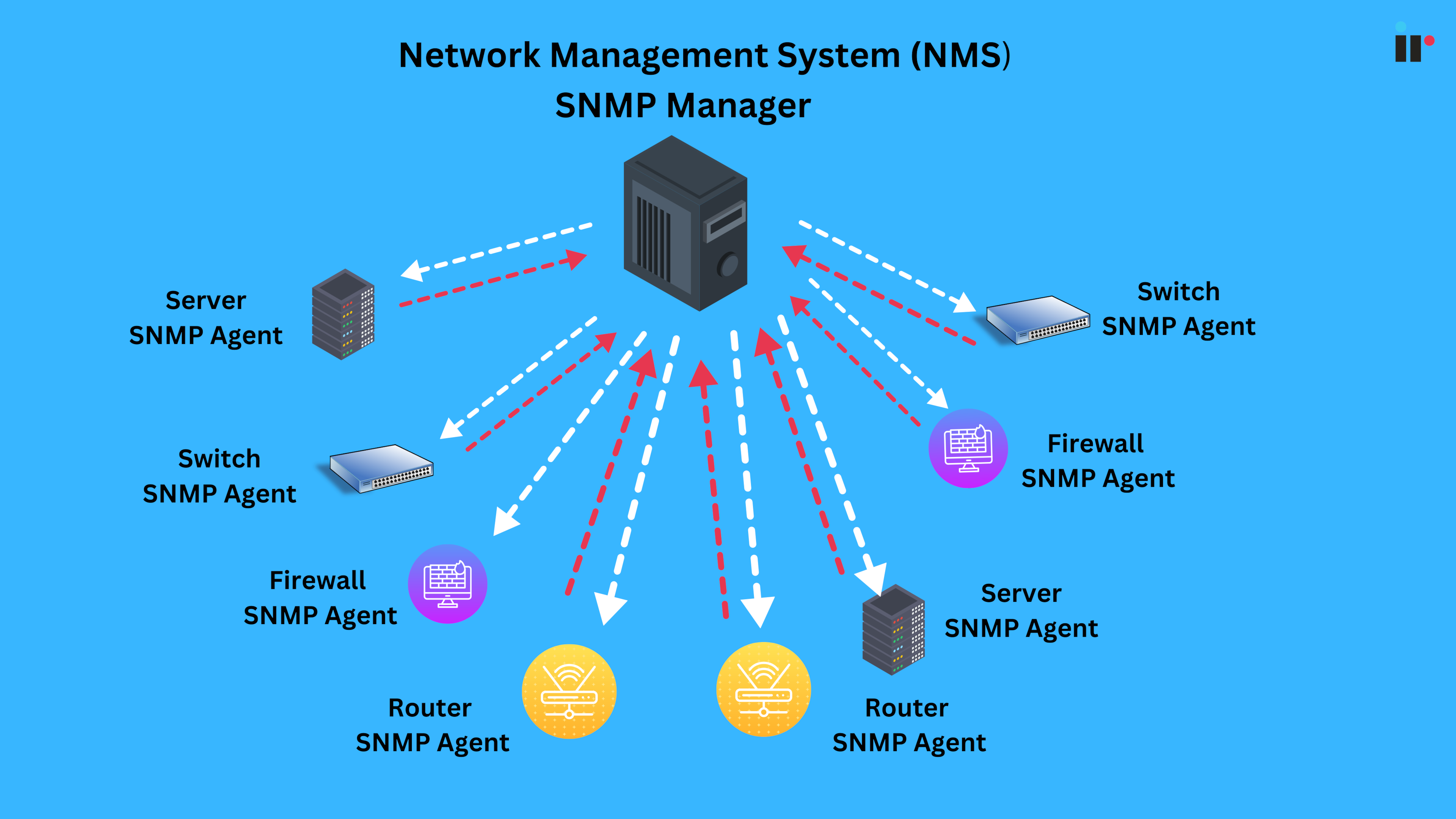
What is Simple Network Monitoring Protocol (SNMP)?
SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol, a vital and powerful application layer protocol that enables the sharing of information among various devices on a network, regardless of the diversity of the hardware or software.
Used to monitor and manage network devices and ensure a network is running smoothly, SNMP monitoring is a key part of network management, and is used by network engineers and administrators to collect information about network equipment, such as routers, switches, and firewalls.
Without SNMP, network management tools wouldn't accurately be able to identify connected devices, monitor network performance, track anomalies and changes, or deliver real-time status updates and network performance problems.
Today, most network devices support SNMP by default, without the network administrator having to do anything other than use an SMNP monitoring tool.
Here are some key aspects of SNMP monitoring
SNMP architecture
SNMP operates on a client-server model, where the server analyzes information from the clients, which are the devices connected to the network. The servers, called managers, collect and process information about devices on the network.
The clients, called agents, are any type of device or device component connected to the network. They can include not just computers, but also network hardware like routers, switches, phones, printers, etc.
How SNMP works and what it can do
SNMP is compatible with most network devices, and most devices include SNMP agents. If a device doesn't have an SNMP agent, network administrators can install one
SNMP can be used to collect data about network changes, determine the status of devices, and configure and control devices remotely.
How SNMP works with data and alerts
SNMP uses object identifiers (OIDs) to identify devices and their status. OIDs are similar to IP addresses, but can be more complex to decipher for large-scale networks.
Software can be configured to alert administrators when thresholds for certain values are exceeded.
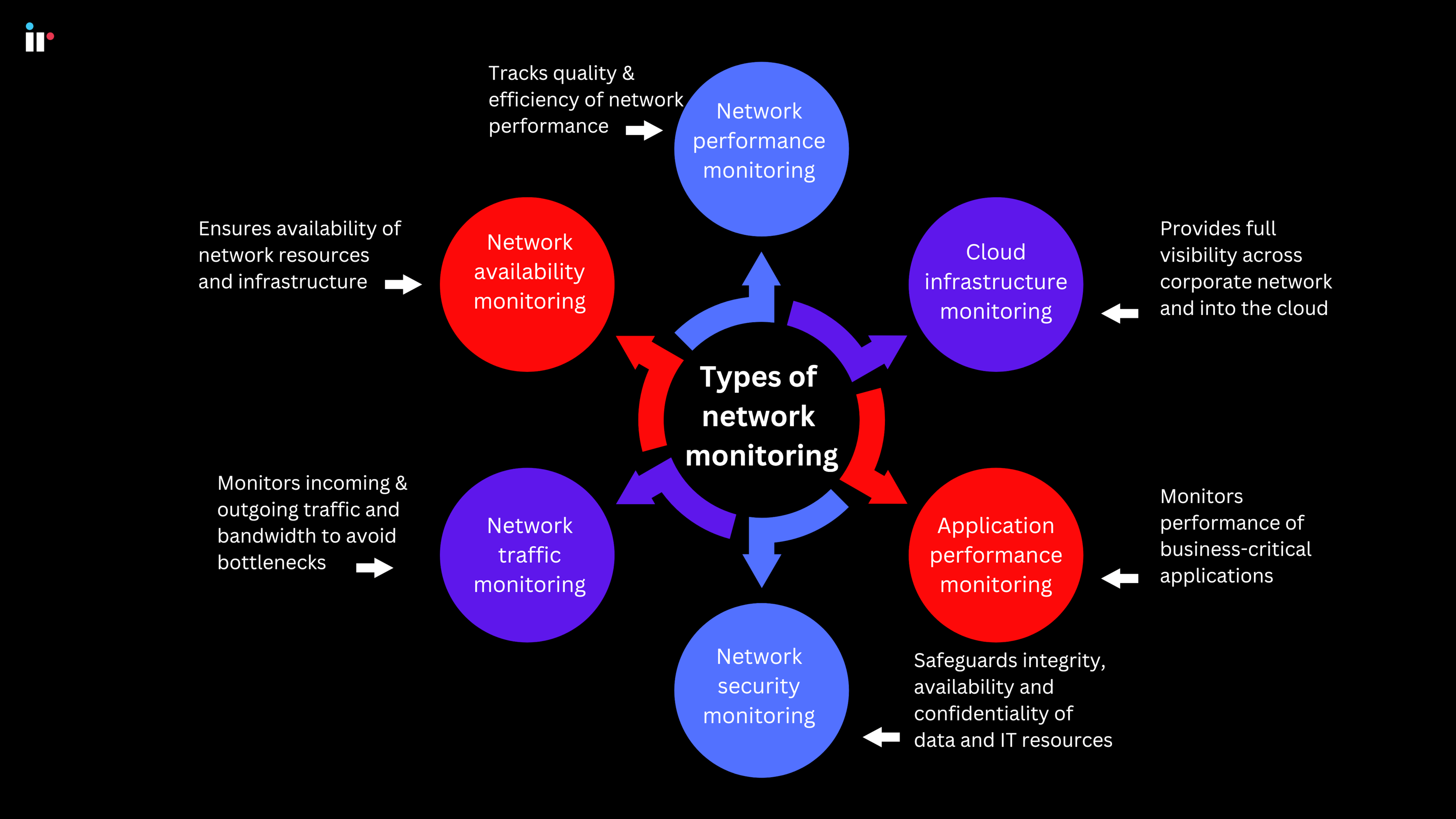
Types of network monitoring
Network monitoring encompasses six basic categories, including:
-
Network performance monitoring
-
Network availability monitoring
-
Traffic monitoring
-
Network Security monitoring
-
Application Performance monitoring
-
Cloud infrastructure monitoring
Network performance monitoring
Network performance monitoring tracks the quality and efficiency of the performance of a network to ensure that it's running at optimal level. This includes analyzing real-time and historical performance data and metrics, such as bandwidth utilization, packet loss, latency and response times. For example:
-
Tracking the speed and reliability of data transfers
-
Analyzing traffic patterns to identify potential bottlenecks
-
Monitoring server response times for web-based applications
Availability monitoring
Availability monitoring, or fault monitoring, helps to ensure the availability of network resources and infrastructure.
It provides real-time detection of issues ranging from hardware failures such as a malfunctioning router to software issues involving a critical web application or connectivity problems. An example is continually sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) pings to all critical network devices and servers to check whether the resource is available.
Availability monitoring tools usually use alerting mechanisms to notify administrators by email, SMS, or dashboard alarms.
Traffic and Bandwidth Monitoring
We've used the analogy of a highway system to describe an enterprise network. Everything slows down to a trickle during rush hour. In order to avoid this, they need to ensure they have ample bandwidth.
Network traffic monitoring uses network trace tools to analyze data from incoming and outgoing traffic across the network to help identify who is using the network and for what purpose.
It also provides bandwidth monitoring, which measures the amount and speed of data transmission over a network to ensure optimal performance and avoid bottlenecks.
Security Monitoring
Network security monitoring is essential for safeguarding the integrity, availability and confidentiality of an enterprise organization's data and other IT resources. Businesses can face steep costs due to security-related disruptions. Types of security monitoring approaches include:
Network logging tools
Used to collect, store and analyze log data from various network devices to maintain a comprehensive record of all activities.
Network detection software
Continuously monitors a network's traffic to identify potential threats or malicious activities in real time.
Network control software
Helps organizations ensure that only authorized activities are permitted and that potential vulnerabilities are patched.
Network surveillance software
Used to vigilantly oversee network activities, ensuring that all data transmissions and activities comply with security policies and track any suspicious or unauthorized activities.
Network device configuration monitoring
Used to check for unwanted or unauthorized changes to the configuration of a device. Changes to ACLs or Firewall rules can seriously affect the way a network operates - and can even render a network unusable.
Application performance monitoring
Application performance monitoring (APM), uses software tools and telemetry data to monitor the performance of business-critical applications.
Enterprise organizations need to ensure that they maintain expected service levels, and that customers receive a positive application experience. APM tools are used to deliver real-time data and insights into the performance of applications, allowing IT teams, DevOps, and site reliability engineers to quickly pinpoint and troubleshoot application issues. Application performance monitoring has many business benefits:
Customer satisfaction
APM tools are used to ensure customer and end-user satisfaction by highlighting common problems in the digital customer journey.
It can determine if changes are beneficial, for example, if a business introduces a new customer service chatbot, APM metrics can measure how many customers had their query solved by using the bot.
Rapid diagnosis
Downtime causes failed customer journeys and financial losses for business operations.
APM can rapidly diagnose and pinpoint the exact location of application performance issues, keeping downtime to a minimum, allowing tech teams to concentrate on developing new applications rather than troubleshooting existing ones.
Reduced operating costs
IT teams use APM tools to determine how much resource, infrastructure, and computing power is actually necessary to keep applications performing optimally, keeping operating costs down.
Effective product development
Application performance monitoring tools are an important part of the process of product development. APM tools can be used in a test or as-live environment to monitor and analyze synthetic traffic, reveal limitations, and identify errors.
Development teams can utilize these valuable actionable insights before an application goes live and fix bugs that would previously only have become evident after a product launch.
Cloud infrastructure monitoring
In many cases, private and public cloud scenarios can use the same types of network monitoring tools implemented on corporate networks. However, many cloud monitoring tools like Solarwinds network performance monitor and Datadog network performance monitoring may not integrate into other third-party tools organizations already use.
Organizations need to address the issue of managing multiple distributed network management services by centralizing their monitoring solutions into a tool that provides full visibility across the corporate network and into the cloud.
Summary: The key benefits of a network monitoring system
The benefits of network monitoring are becoming evident as more and more enterprise organizations adopt remote or hybrid work models. It's vital that both your on-premise operations and your off-site network performs optimally, and that your monitoring tools can identify all network performance issues.
The most important benefits of using network monitoring software include:
Identifying issues and anomalies at any point throughout the network
A network monitoring solution can quickly locate a problem anywhere in the network. Monitoring your network performance can accurately pinpoint the cause and source of a network problem, where and when it occurred, and who needs to fix it.
Network monitoring software proactively monitors your entire network to analyze performance data and detect any performance changes that could be problematic to users before they occur.
Providing historical and baseline data
With the availability of baseline data, a network can continually and automatically compare data.
If network monitoring systems pick up degraded performance issues within the network infrastructure, an alert is automatically sent so that IT teams can immediately address the problem.
Historical data gives you a comparison point to determine optimal network performance or identify poor performance. It also enables you to troubleshoot network problems from past events.
Better utilization of IT resources
Without network monitoring tools to oversee performance, a network outage can seriously affect productivity. IT managers face the problems of having to shift their attention from one important project to a crisis issue with little or no warning.
A key benefit of network monitoring systems is that they reduce the manual process of locating and fixing problems for IT teams, and prevent wasting valuable time and resources which can instead be allocated to more critical projects.
What to look for in network monitoring tools
Today's monitoring tools are advanced solutions with comprehensive monitoring and reporting capabilities designed to help you address key performance metrics.
The most comprehensive monitoring tools should be capable of ensuring your network is functioning correctly and delivering uninterrupted services.
Ideally, the features of these tools should include all or most of the following:
-
Built-in reporting system
-
Bandwidth utilization monitoring
-
Intuitive centralized dashboards
-
Network traffic monitoring
-
Dynamic and intelligent network mapping
-
Automatic alerting
-
User experience monitoring
-
Automatic recovery
-
Remote administration
-
Wireless network performance metrics monitoring
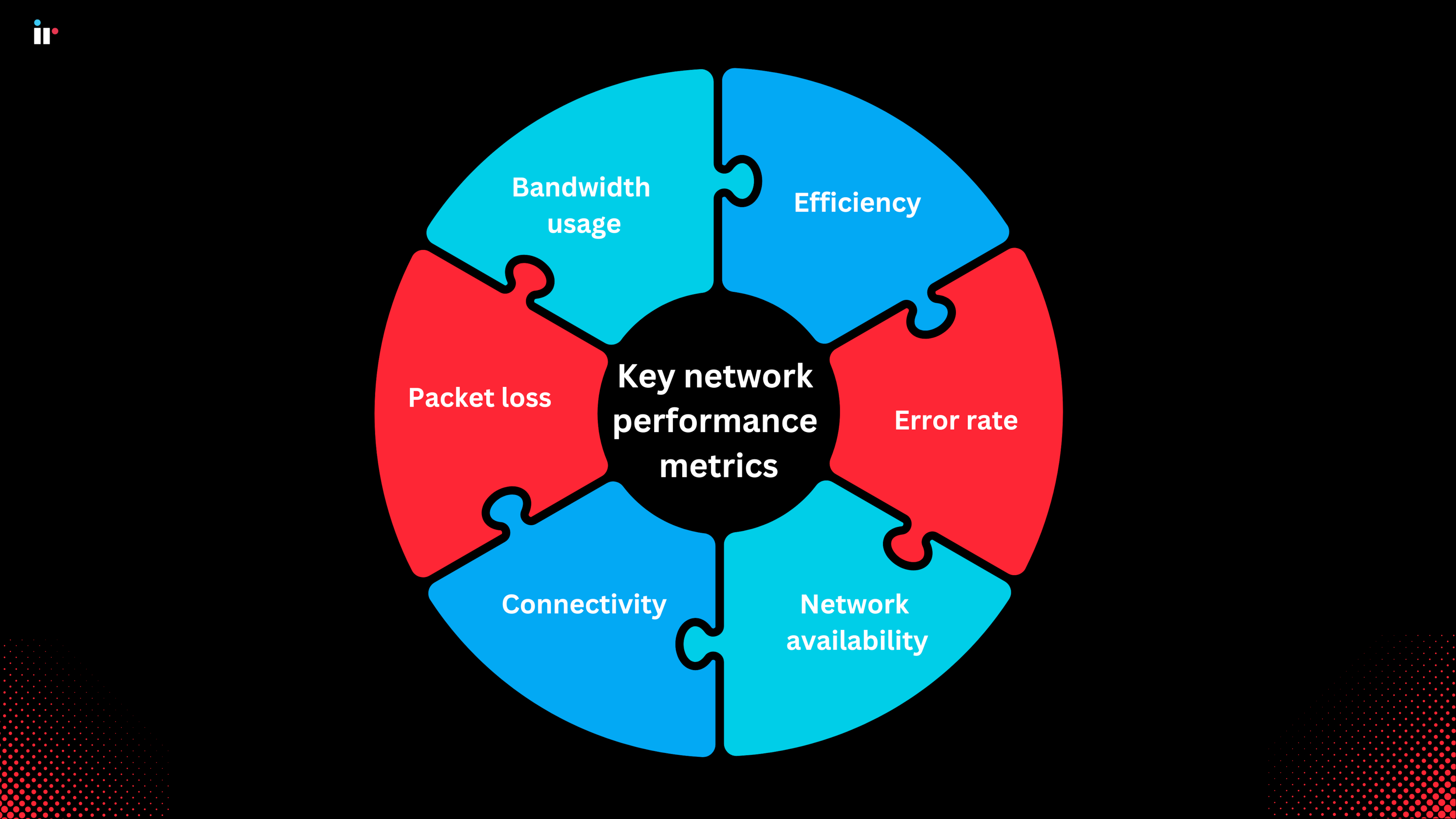
Key network performance metrics
Network monitoring tools and the key metrics you need to monitor, will identify performance values that directly affect your organization's network.
The following 6 key network metrics can help you monitor network performance and detect network problems in real-time.
-
Bandwidth usage: Bandwidth is extremely important in terms of efficient network performance. As mentioned earlier, exceeding bandwidth limit slows traffic, and causes network congestion. Network monitoring solutions warn you via instant notifications if you exceed bandwidth threshold.
-
Packet loss: Data packet loss refers to the data packets lost during the journey between two destinations, and can adversely affect user services. TCP, the Transmission Control Protocol, can monitor lost data packets and ensure that they reach their destination.
-
Efficiency: Efficiency, or throughput/time ratio, enables you to measure the data transfer rate of your network connections in different areas. It measures the real amount of data packets sent over the network and detects areas with throughput and re-transmission.
-
Network availability: Network availability ensures the consistency of the service you provide to end-users, enabling you to observe the uptime of your network within a certain period.
-
Connection: This metric allows you to check the connectivity between devices and nodes in your network. You can prevent service interruptions by detecting malfunctioning devices and nodes using the connection metric.
-
Error rate: The percentage of requests that didn't receive a response or failed. This is an important metric for identifying issues and bottlenecks that affect system performance.
Summary: Best practices for effective network monitoring
Monitoring your network's health and minimizing downtime are essential, and these form the cornerstone of network management. Formulating best practices allows network admins to efficiently fine-tune their networks to establish clear standards of network performance and quickly identify issues as they occur. Here are some of the most important best practices in network management.
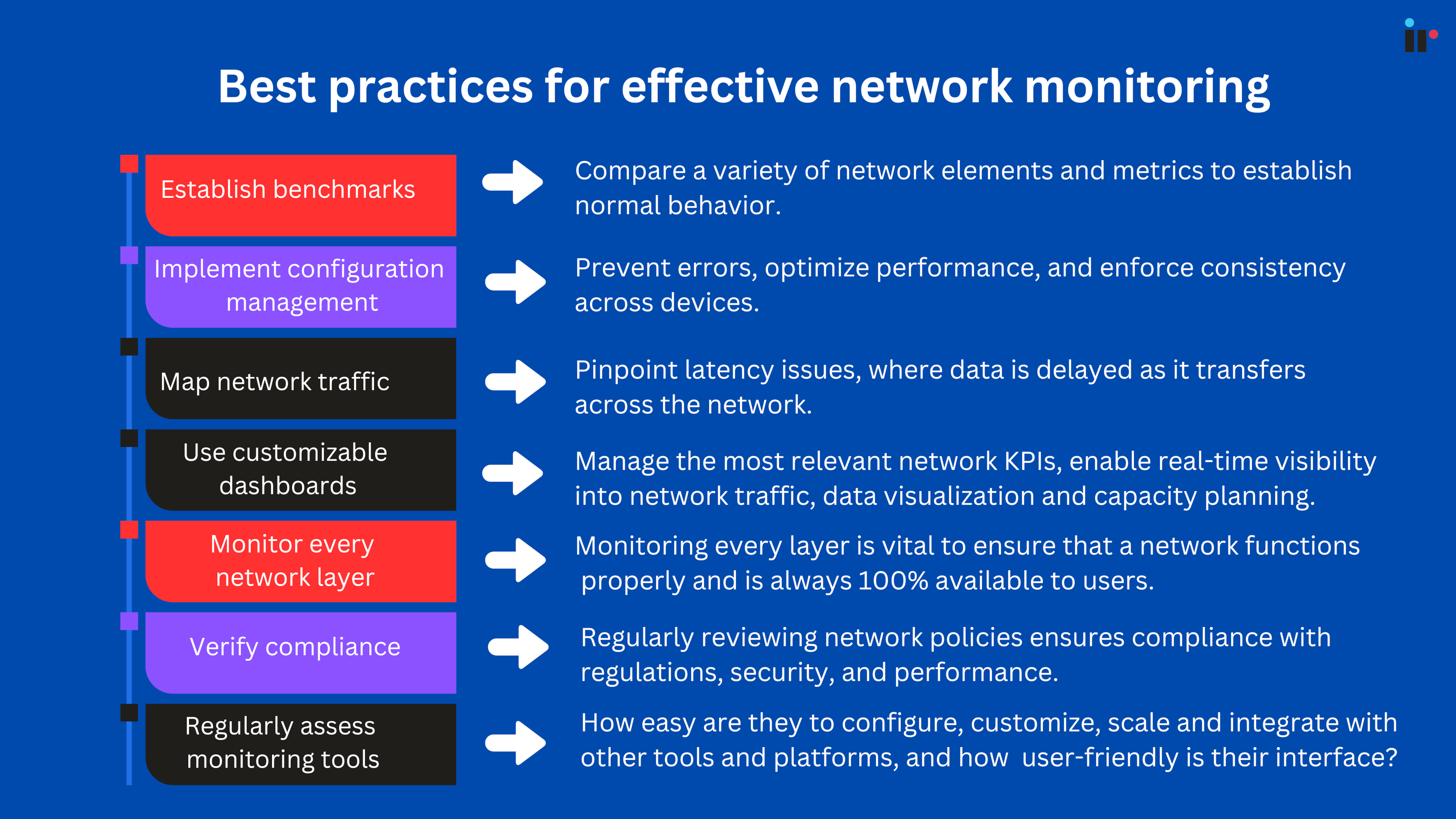
Establish benchmarks
Benchmarks are essential to compare a variety of network elements and metrics to establish normal behavior.
In effect, they provide a reference point for network administrators to apply a diverse set of vital elements and metrics that include the following:
-
Bandwidth.
-
CPU usage.
-
Memory consumption.
-
Error rates.
-
Latency.
-
Packet loss.
-
Rack temperatures.
-
Device operation.
Implement configuration management
Automated configuration management tools can help prevent errors, optimize performance, and enforce consistency across devices.
Implemented properly, you can configure your network device settings to match your organization’s needs, including software and firmware updates, applying security patches, and maintaining proper configurations.
Effective configuration management prevents errors and optimizes network performance, providing consistency across devices, reducing the risk of misconfigurations, and helping maintain compliance with organizational policies and standards.
Map network traffic
By mapping the traffic on a network, admins can pinpoint latency issues, where data is delayed as it travels across the network.
A network topology map can help to regularly monitor data exchanges, using tools such as ping and traceroute. Ping is a command-line tool that measures round-trip time, while traceroute shows the path of data packets and latency at each exchange. Network engineers can accurately respond to issues and use these tools to address bottleneck issues, calculating the processing power required for programs and data on a network.
Use customizable dashboards
Customizable dashboards are a boon for IT operations, as they enhance visibility through real-time graphs and reports on component performance along with email and text alerts.
During the initial setup, these notifications can be integrated with AIOps platforms to reinforce best practices and accelerate issue resolution using root-cause analysis.
Dashboards help network admins to track and monitor and proactively manage the network KPIs that are most relevant to them, enabling real-time visibility into network traffic, data visualization and capacity planning.
Monitor every network layer
Networks are made up of a number of layers, and monitoring every layer is vital for ensuring that a network is functioning properly and is always 100% available to users.
Network components
This includes routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and VMs. Monitoring each component helps ensure that they are all working properly.
Network performance
This is vital to identify performance issues and bottlenecks early, which can prevent network downtime or failures.
Network availability
Monitoring a network's availability can help ensure that the network is accessible to users when they need it.
Security vulnerabilities
Monitoring for security breaches and vulnerabilities is critical to avoid compromising the network's performance.
Verify compliance
Regularly reviewing network policies ensures compliance with regulations, security, and performance.
Every organization is responsible for instituting its own compliance monitoring program. Network management tools can monitor compliance risks using dashboards, compliance software and a high degree of automation to help streamline the compliance management process and offer more oversight.
Regularly assess monitoring tools
Assessing your current network monitoring tools and identifying their strengths and weaknesses ensures that tools are up-to-date with the latest features and security patches.
Determine how often they perform network scans, data updates, and how accurately they detect and report network issues. How easy are they to configure, customize, and integrate with other tools and platforms, and how well do they scale to support your network size, complexity, and diversity - and how user-friendly is their interface?
Why choose IR Collaborate
IR Collaborate offers comprehensive, multi-tenant and multi-vendor monitoring and support, real time insights and customizable displays, providing end to end visibility across all UC ecosystems.
Specialized (domain-centric) tools with advanced features, like IR Collaborate will give you unparalleled network security, network traffic monitoring and comprehensive performance insights throughout your entire network.
In a complex, multi-vendor unified communications ecosystem, real time network monitoring is essential to help you avoid, and quickly find and resolve performance issues across your on-premises, cloud or hybrid environments.
IR Collaborate's suite of performance management solutions are utilized by hundreds of the world's largest organizations to optimize their business-critical systems.
Our world-class network monitoring solutions provide deep insights, comprehensive monitoring and 24/7 support to keep payment hubs, unified communications ecosystems and contact centers running as they should. Some of the key features of our software include:
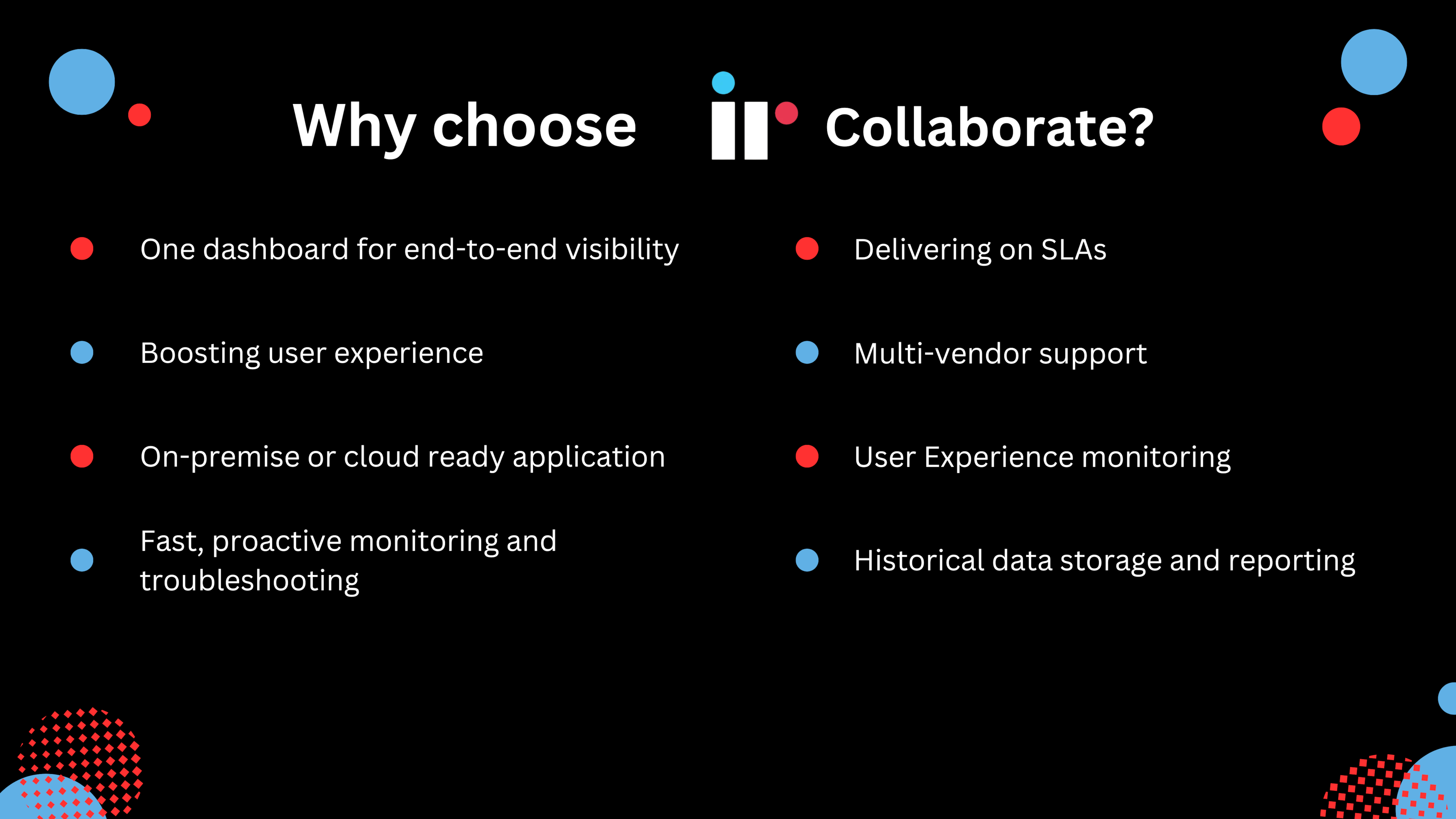
One dashboard for end-to-end visibility
Broad multi-vendor coverage means you can streamline IT processes and operations with visibility across your entire environment from a single pane-of-glass.
Boosting user experience
Improve the performance of video conferencing and collaboration tools to optimize productivity and keep your modern workforce connected.
On-premise or cloud ready application
Deploy our versatile solutions in the cloud, on premises or as a hybrid model, to suit your enterprise unified communications needs.
Fast, proactive monitoring and troubleshooting
Find and fix root-cause of problems quickly so you can maximize system performance and minimize user impact.
Delivering on SLAs
Organizations can ensure customer satisfaction and deliver on SLAs throughout their network operations, with real-time alerts and rapid troubleshooting, meaning faster, more efficient problem resolution and higher uptime, with the reporting and evidence to back it up.
User Experience monitoring
The power to monitor the end-user experience, providing insights into application responsiveness, website loading times, and other factors affecting user satisfaction.
Historical data storage and reporting
The storage of historical data, allows administrators to analyze trends over time. This data is valuable for capacity planning, troubleshooting recurring issues, and assessing the impact of changes to the network.
Multi-vendor support
IR Collaborate caters to diverse customer needs, providing efficient coverage with support for Microsoft, Cisco, Zoom, Avaya and others, integration with ServiceNow, as well as insight across networks, SBCs, and endpoints.
Find out more about how IR Collaborate can help increase network uptime


